What Is the Longest River in Australia? Discover the Mighty Murray River
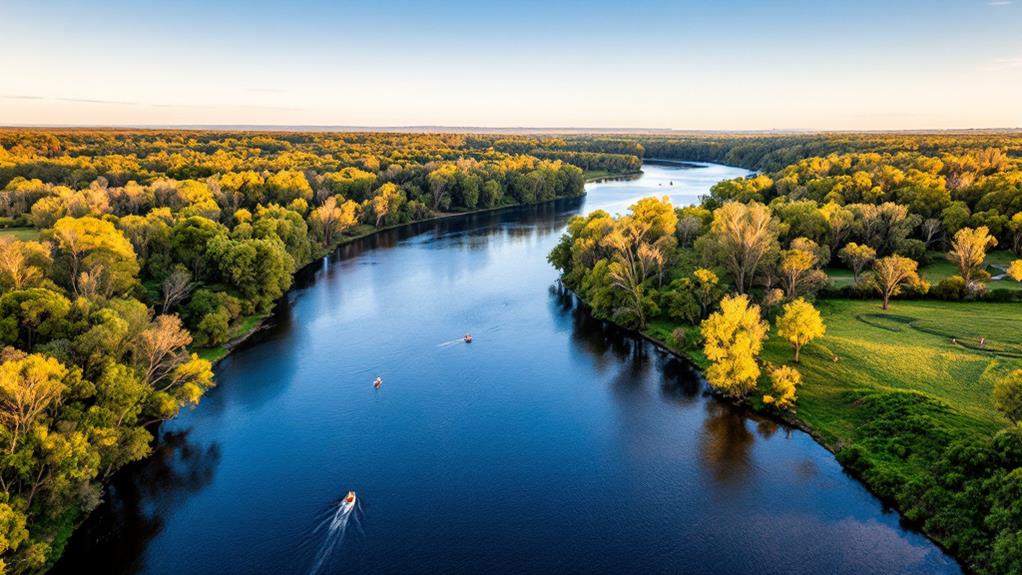

You're in for a treat as you uncover the mighty Murray River, Australia's longest river. Stretching an impressive 2,508 kilometers, it begins in the Australian Alps and creates a natural border between New South Wales and Victoria. This river sustains nearly 2,000 kilometers of navigable waters, making it among the longest of its kind globally. Historically significant and culturally sacred to Aboriginal Australians, the Murray plays a crucial role in agriculture and ecosystems. It supports diverse wildlife within the Murray-Darling Basin. As you look further, hold tight for insights into its historical and cultural significance.
Geography and Length
The Murray River, a winding ribbon of water, claims the title of Australia's longest river at 2,508 kilometers (1,558 miles). It gracefully rises in the Australian Alps, then courses northwest, defining much of the border between New South Wales and Victoria. As you investigate its remarkable geography, you'll find the Murray River's expedition is a demonstration of nature's grandeur, offering a lifeline across vast landscapes.
Notably, the river provides nearly 2,000 kilometers of navigable waters, making it the third longest globally in this regard. This impressive stretch guarantees that the Murray River is not only a geographical marvel but also an essential artery for transport and recreation. As part of the expansive Murray-Darling Basin, which spans over 1 million square kilometers, the river supports around 1.5 million households and businesses. Its waters, enriched by significant tributaries like the Murrumbidgee, Darling, Lachlan, Warrego, and Paroo Rivers, sustain diverse ecosystems and communities.
Unquestionably, the Murray River's geography and length make it a cornerstone of Australian natural history, intertwining the regions of New South Wales and Victoria in a shared reliance on its abundant resources.
Historical Significance
In 1830, Captain Charles Sturt christened the Murray River, honoring Sir George Murray and marking its recognition by European adventurers. This naming was just the beginning of the river's historical significance. The Murray River became a crucial artery for transport and commerce, especially with the introduction of paddle steamers in 1853. By the late 19th century, up to thirty paddle steamers navigated its waters, underscoring the river's importance in connecting communities and supporting trade.
Geological studies reveal the river's ancient past, with its natural history extending back approximately 130 million years. These studies highlight the environmental transformations the region has undergone, including the days of Ancient Lake Bungunnia between 2.5 and 0.5 million years ago. These findings provide insight into how the river has shaped current cultural landscapes.
The Murray River is fundamental for agriculture, serving as a precious water source for the fertile lands it nourishes. Its historical significance is reflected in the economic and cultural development of the regions it traverses.
- 1830: Captain Charles Sturt named the river.
- 1853: Paddle steamers began operating.
- 130 million years: River's geological history.
- Crucial for agriculture: Supports regional development.
- Cultural landscapes: Shaped by the river's presence.
Cultural Importance

Beyond its historical role in commerce and agriculture, the Murray River echoes deeply within the cultural fabric of Australia. For Aboriginal Australians, the river is more than just a waterway; it's a sacred entity woven into their ancestral stories. One such tale is that of Ngurunderi, who created the Murray River while pursuing the Murray Cod. These creation myths, shared among diverse Aboriginal language groups, underline the river's enduring cultural significance across generations.
For over 40,000 years, the Murray River has been a crucial source of sustenance and connection for Indigenous communities. It's not merely a physical resource but a cultural heritage site that embodies the spiritual and cultural relevance of their way of life. Understanding these perspectives requires exploring cultural resources and literature that investigate the Aboriginal history surrounding the river.
As you learn about the Murray River, consider the collaborative efforts between community members and Traditional Owners who focus on preserving its health and cultural heritage. These initiatives highlight the environmental stewardship important to maintaining the river's cultural significance. Supporting these efforts guarantees that the Murray River continues to nourish both the land and the spirit of its people.
River Ecosystems
Amidst Australia's vast landscapes, the Murray River cradles a rich array of ecosystems teeming with life. These ecosystems include the iconic river red gum forests, which are fundamental habitats for a variety of wildlife, including endangered species like the Murray crayfish. The river's biodiversity is significant, but it's been compromised over the years. Since European settlement, the Murray River's health has suffered, with only 58% of its natural flow recorded as of 2010. This decline affects both the ecosystem and the biodiversity it supports.
The Murray-Darling Basin, covering over 1 million km², plays an important role in maintaining ecological balance and supplying water to 1.5 million households and businesses. However, extreme droughts and regulated flows have stressed the river's natural ecosystems, raising concerns about the sustainability of flora and fauna along its banks. To combat these challenges, conservation efforts are underway, focusing on restoring the river's health to support its diverse ecosystems.
- River red gum forests provide significant habitats for wildlife.
- Only 58% of the river's natural flow remains.
- The Murray-Darling Basin is fundamental for ecological balance.
- Extreme drought conditions stress the river's ecosystems.
- Conservation efforts aim to restore the river's health.
River Management
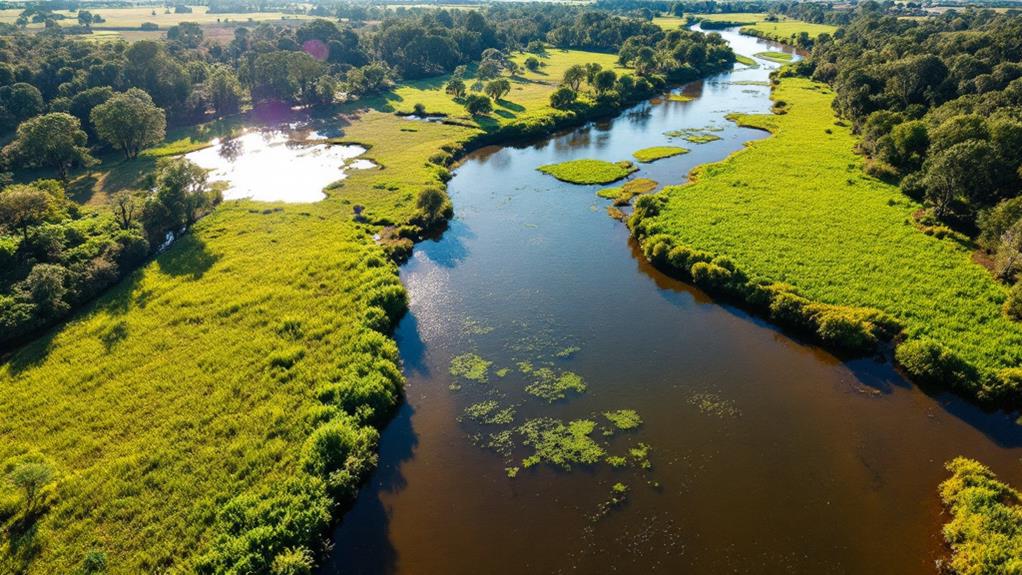

Thanks to extensive river management strategies, the Murray River's flow is controlled through water releases from four major dams. This regulation guarantees a consistent supply for both agricultural and recreational needs. The infrastructure supporting this management includes 16 storage weirs and 15 navigable locks. These structures facilitate irrigation and navigation while working to maintain ecological balance. However, this balance is delicate, as the river system received only 58% of its natural flow as of 2010. This statistic underscores the challenges in sustaining river health amid increasing demands.
River management practices prioritize sustainable usage, guaranteeing the Murray River can continue supporting the needs of 1.5 million households and businesses relying on it as a essential water source. Continuous efforts are in place to monitor and maintain water quality, which is fundamental for the health of the surrounding ecosystems. Without such measures, the river's ability to support diverse life forms and human activities would be compromised. By focusing on sustainable usage and careful regulation, you can help protect the Murray River, guaranteeing its water quality and ecological balance are preserved for future generations.
Community Engagement
Community engagement is fundamental for the preservation and health of the Murray River. By participating in local initiatives, you help maintain its cultural heritage and contribute to the community's identity. Local volunteers are invaluable, preserving the river's history and fostering a sense of belonging. Engagement initiatives aim to strengthen connections among residents, local organizations, and stakeholders, ensuring everyone's voice is heard.
Working closely with Traditional Owners is imperative. Their cultural heritage and land stewardship practices are integrated into river management strategies, honoring their deep connection to the river. Regional Engagement Officers organize monthly discussions, providing a platform for community members to share ideas and collaborate on river health initiatives. This collaboration is crucial for promoting environmental awareness and encouraging sustainable practices.
You can make a difference by participating in community events and activities that highlight the importance of the Murray River to local ecosystems and economies. These efforts are not just about preserving the river today but ensuring its liveliness for future generations.
- Engage in local volunteer programs
- Attend monthly discussions for river health initiatives
- Support Traditional Owners in cultural heritage projects
- Participate in events promoting environmental awareness
- Advocate for sustainable practices in your community
Recreational Activities
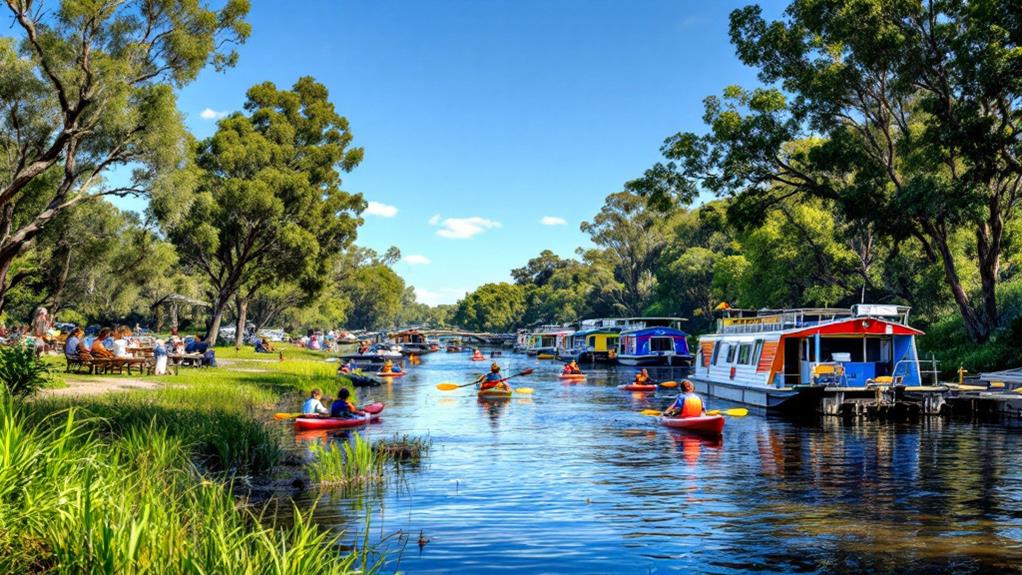

While engaging with the community around the Murray River is significant, enjoying the recreational activities it offers is likewise rewarding. Imagine yourself paddling through nearly 2,000 km of navigable waterways, where canoeing and boating provide a sense of adventure and freedom. The Murray River invites you to investigate its vast and serene waters, offering countless opportunities for exploration.
Along the riverbanks, you'll find excellent fishing spots that draw anglers in search of native species like Murray cod and yellowbelly. Cast a line and experience the thrill of fishing in one of Australia's most iconic rivers. If you're seeking a deeper connection with nature, camping along the Murray River is a perfect choice. Numerous designated sites allow you to engage yourself in the area's natural beauty and tranquility.
Eco-tourism initiatives offer sustainable ways to investigate the Murray River, with guided tours that showcase the unique ecosystems and cultural significance of the region. Participate in river regattas or fishing competitions, where events and festivals celebrate the Murray River's rich cultural heritage. Regardless of whether you're a local or a tourist, these recreational activities promise unforgettable outdoor experiences along Australia's longest river.
Major Settlements
The Murray River corridor is dotted with lively settlements that are essential to the region's economy and culture. Among these major settlements are Echuca, Mildura, and Renmark, each offering unique contributions to the area's vibrancy. Echuca, with its historic port and paddle steamer operations, stands as a lighthouse of tourism, drawing visitors enthusiastic to investigate its rich past. On the other hand, Mildura thrives on agriculture, renowned for its lush wineries and bountiful produce. This city not only enhances the local economy but also attracts wine enthusiasts from around the globe.
Renmark, known as Australia's primary irrigation district, is significant in the Murray River's agricultural production, especially in the fruit and wine industries. Its fertile lands make it a cornerstone for farming and viticulture, supporting both the local community and the broader economy.
Living along the Murray River means you're part of a diverse and dynamic community. Here's what makes these settlements significant:
- Echuca: Historic charm and thriving tourism.
- Mildura: Agricultural powerhouse with flourishing wineries.
- Renmark: Leader in irrigation and wine production.
- Albury-Wodonga: Key urban center with diverse demographics.
- Swan Hill: Reflective of rich cultural and population diversity.