What Hemisphere Is Australia In? Understanding Australia’s Global Position

You'll find Australia entirely in the Southern Hemisphere. It's positioned distinctly between the Indian and Pacific Oceans, framing its diverse environments. This southern location means Australia enjoys warmer temperatures and exceptional climates, from tropical in the north to temperate in the south. Its separation from Asia by the Arafura and Timor Seas results in remarkable flora and fauna, including many endemic species. This positioning has deeply influenced Australia's maritime culture and biodiversity. Understanding Australia's location helps explain its weather patterns, cultural heritage, and significant global role. There's much more to investigate about this fascinating continent.
Australia's Geographical Location
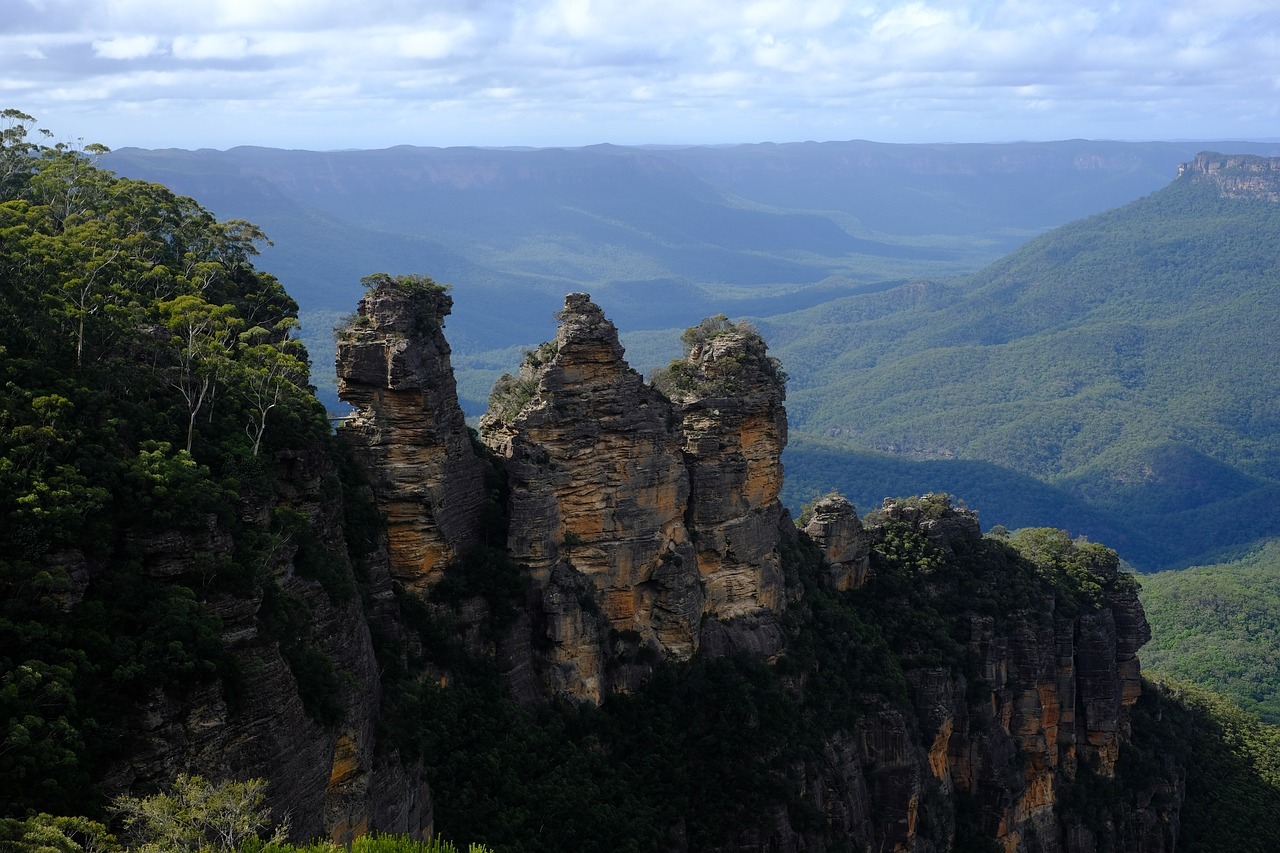
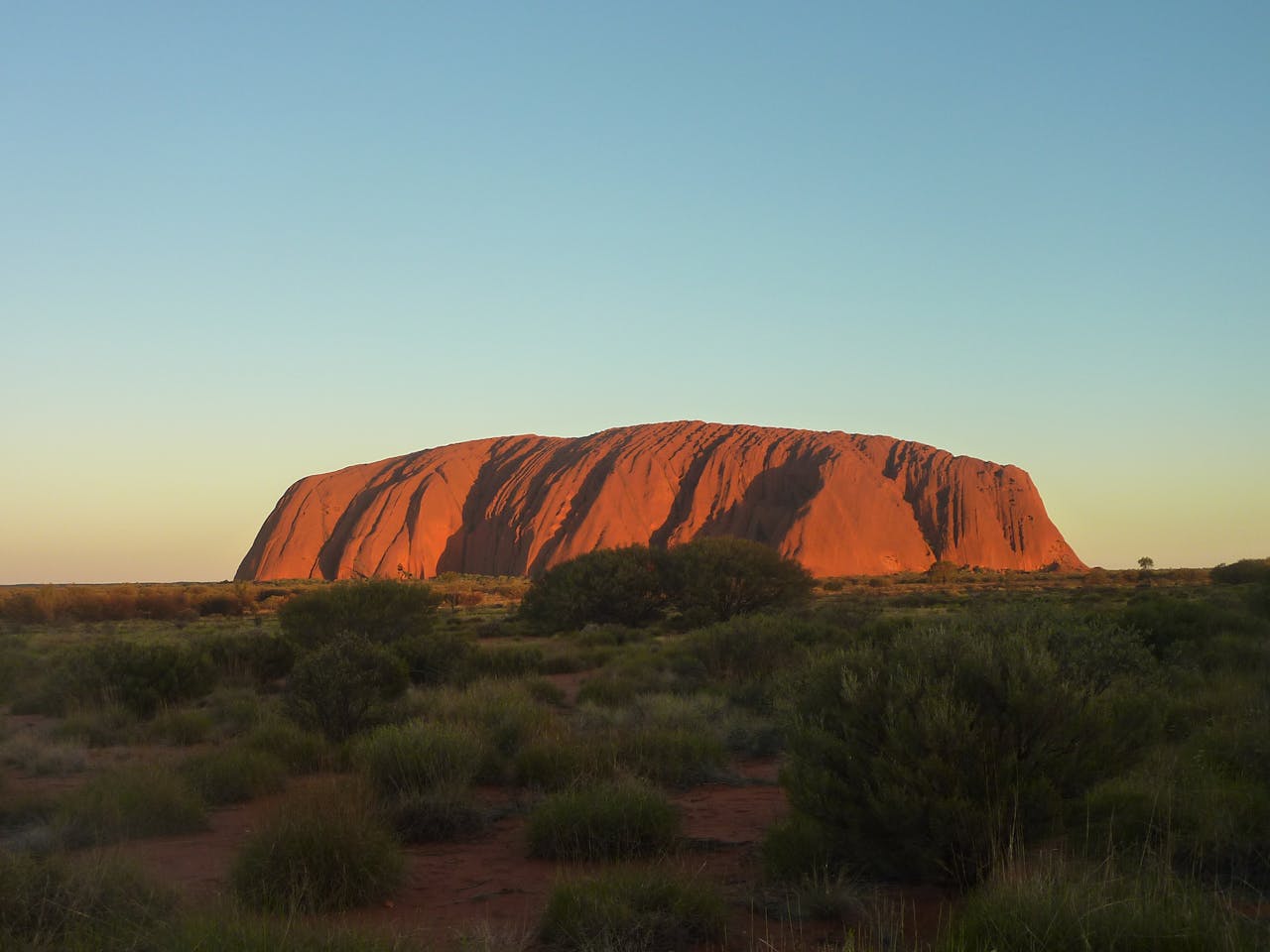
Positioned entirely in the Southern Hemisphere, Australia's unique location between latitudes 10.45°S and 43.39°S sets it apart. It stretches across the Eastern Hemisphere, with longitudes ranging from 113.9°E to 153.39°E. As the largest country on the Australian continent, it's distinctively situated between the Pacific Ocean to the east and the Indian Ocean to the west. This geographical positioning not only shapes its natural landscapes but also influences its ecological and cultural development.
You'll find Australia to be the smallest of the seven continents, covering about 7.69 million square kilometers. Despite its size, its position between two vast oceans and separation from Asia by the Arafura and Timor Seas creates a diverse environment. This separation plays a significant role in the uniqueness of Australia's flora and fauna, distinct from those found in nearby regions.
Australia's location as a Southern Hemisphere giant surrounded by the Indian and Pacific Oceans contributes to its rich maritime culture. Understanding its geographical positioning is key to appreciating how this vast land manages to maintain its identity and influence in the world. As you investigate Australia's position, you'll uncover a nation shaped by its distinct place on the globe.
Hemispherical Influence on Climate
Within the sweeping hug of the Southern Hemisphere, Australia experiences a climate distinctly shaped by its ocean-dominated surroundings. The Southern Hemisphere's high ocean-to-land ratio means that water covers approximately 60.7% of its surface. This extensive water coverage plays a crucial role in regulating temperatures across Australia, resulting in milder climate patterns compared to those in the Northern Hemisphere. As the oceans heat and cool more gradually than land, Australia benefits from a more temperate climate, with gentler seasonal shifts.
In Australia, geographical influences are profound. The northern regions bask in tropical climates, characterized by warm temperatures and distinct wet and dry seasons. Meanwhile, the southern parts enjoy temperate conditions, where seasonal variations are more pronounced, but still moderated by the vast surrounding oceans. Furthermore, the sun's path from east to west via the north affects local climate and daylight, contributing another layer of complexity to Australia's diverse weather patterns.
Understanding these hemispherical influences helps you appreciate the unique climate zones within Australia. It's this delicate balance of ocean and land, shaped by geographical and seasonal factors, that makes Australia's climate both fascinating and distinctive.
Unique Flora and Fauna

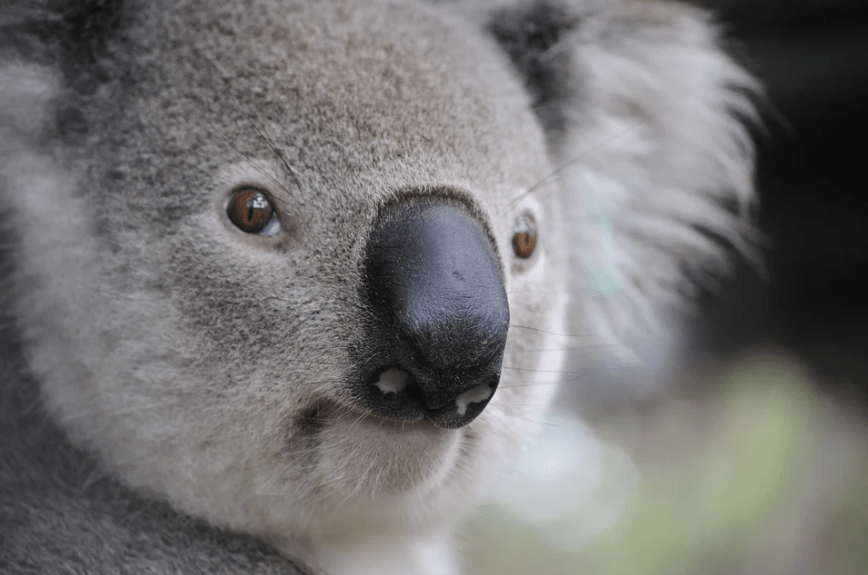
Australia's biodiversity encapsulates a world of wonder, offering a glimpse into a domain where evolution has crafted unique flora and fauna. With over 1 million species of plants and animals, about 80% of these are found nowhere else on Earth. This makes Australia a wealth of unique species, illustrating the incredible diversity within its ecosystems. Iconic animals like the kangaroo, koala, and platypus showcase their remarkable adaptations to the continent's diverse environments, from arid deserts to lush rainforests.
The Great Barrier Reef stands as a proof of Australia's rich marine biodiversity. As the largest coral reef system globally, it supports over 1,500 species of fish and 400 species of coral, making it a lively underwater ecosystem. On land, eucalyptus trees dominate many landscapes, playing an essential role in ecosystems and serving as the primary food source for koalas.
However, with around 500 species of animals and plants threatened or endangered, Australia's status as a biodiversity hotspot underscores the urgent need for conservation. Protecting these unique ecosystems and the flora and fauna they support is key for maintaining the natural heritage and ecological balance of this extraordinary continent.
Cultural and Historical Insights
While Australia's natural beauty captivates with its unique ecosystems, the continent's cultural and historical richness offers a likewise compelling narrative. In the south of the Hemisphere, where Australia is located, you'll find that Australian culture is a tapestry woven from its Indigenous heritage and lively multicultural influences. Aboriginal peoples have lived here for over 65,000 years, nurturing a deep connection to the land through traditions, art, and diverse languages.
European settlement began in 1788 when the Initial Fleet, led by Captain Arthur Phillip, arrived and established New South Wales as a penal colony. This marked the start of a transformative period in Australian history. As you investigate further, you'll uncover the significant milestone in 1901 when Australia's Federation unified the colonies into the Commonwealth of Australia, creating a federal parliamentary democracy that shaped the nation's modern identity.
Today, Australian culture thrives on its multiculturalism, with around 30% of the population being foreign-born. This diversity is reflected in the country's food, festivals, and arts. Historical events, like the Anzac Centenary, play a vital role in fostering national identity, celebrating the contributions and sacrifices of Australians in global conflicts.
Economic and Global Relations
In the domain of economic and global relations, Australia stands as a formidable player with its highly developed market economy. It's ranked among the top 15 countries globally for GDP, largely due to its notable exports of natural resources, especially minerals and agricultural products. Despite being located in the Southern Hemisphere, Australia maintains strong trade relations with Northern Hemisphere nations, particularly East Asia. China, its largest trading partner, accounts for over 30% of Australia's total exports.
Australia's economic policies focus on diversification to guarantee long-term stability. The country addresses challenges like housing affordability and its dependency on commodity exports. By doing so, it builds resilience within its economy. As a member of prestigious international organizations like the UN, G20, and OECD, Australia actively participates in global governance.
With a commitment to sustainability, Australia engages in global discussions on climate change, balancing economic growth and environmental conservation. This dedication reflects its broader Commonwealth values, integrating economic and environmental goals. Through these efforts, Australia not only strengthens its own economic standing but also contributes considerably to shaping a sustainable future for the global community.




